Mixer
The Mix Page in Reliq is closely integrated with the Matrix Page, providing a dedicated interface for controlling the attenuation of each input and output. With 32 high-resolution analog amplitude controls—16 for inputs and 16 for outputs—the Mix Page enables precise control over signal levels.
Attenuation operates on two levels: input attenuation and output attenuation. Adjusting the output attenuation controls the summed signal level at each output, while modifying the input attenuation affects the amplitude of that input across all connected outputs. These adjustments are visually represented in the graph below.
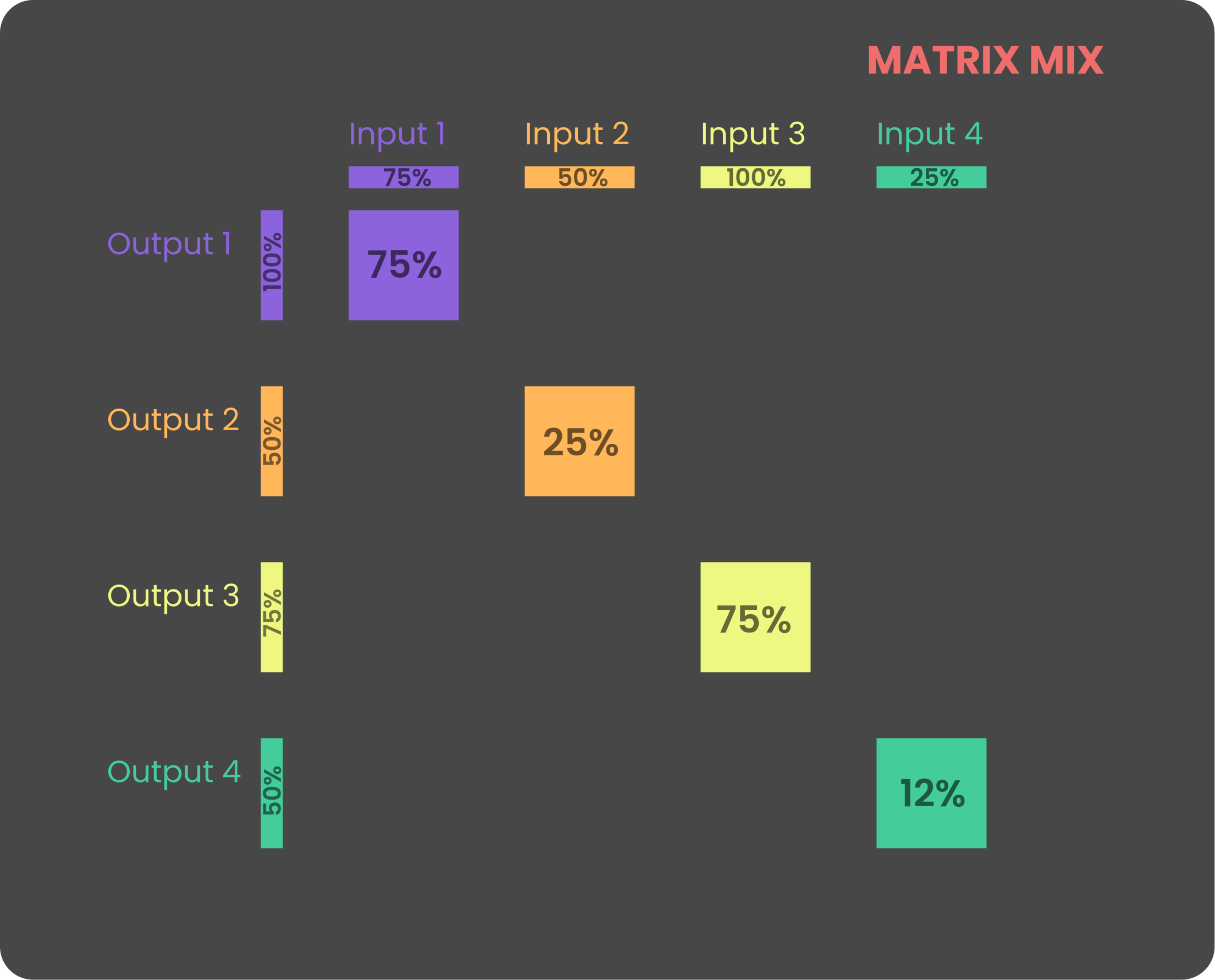
The Reliq mixer operates fully in the analog domain and is factory-calibrated to provide unity gain when both input and output attenuations are set to 100%. However, due to the analog nature of the system, factors such as temperature and environmental conditions may cause slight variations in gain.
The Mix Page plays a vital role in shaping the mix within each routing configuration. Every mix setting is saved as part of the active routing and can be dynamically sequenced using the Matrix Sequencer (refer to the Sequencer chapter for details), allowing for real-time control and smooth transitions between different mix configurations.
Interface Overview
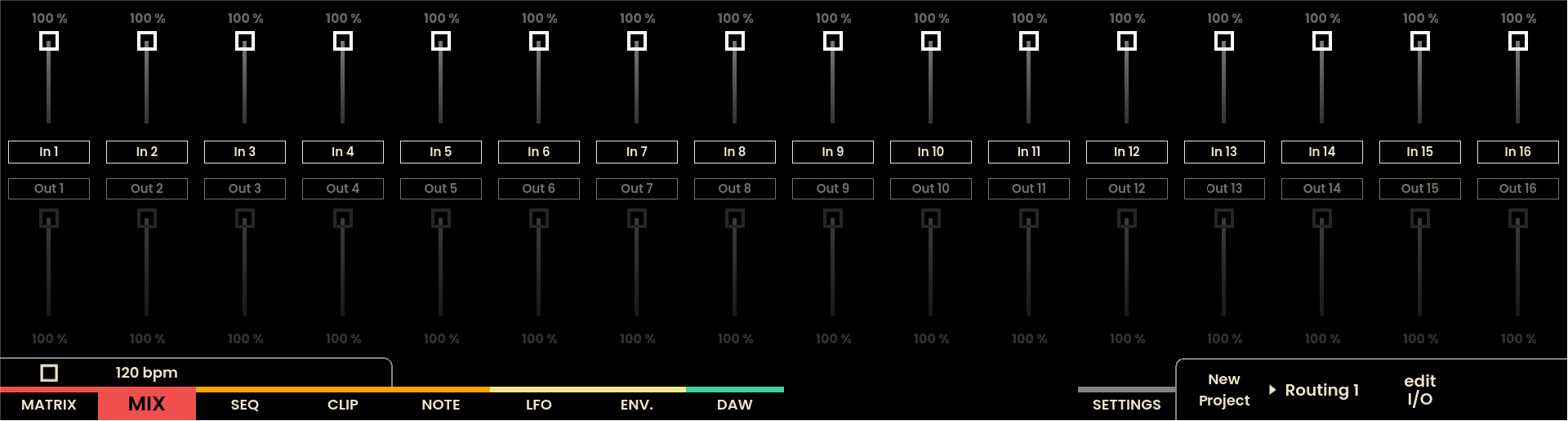
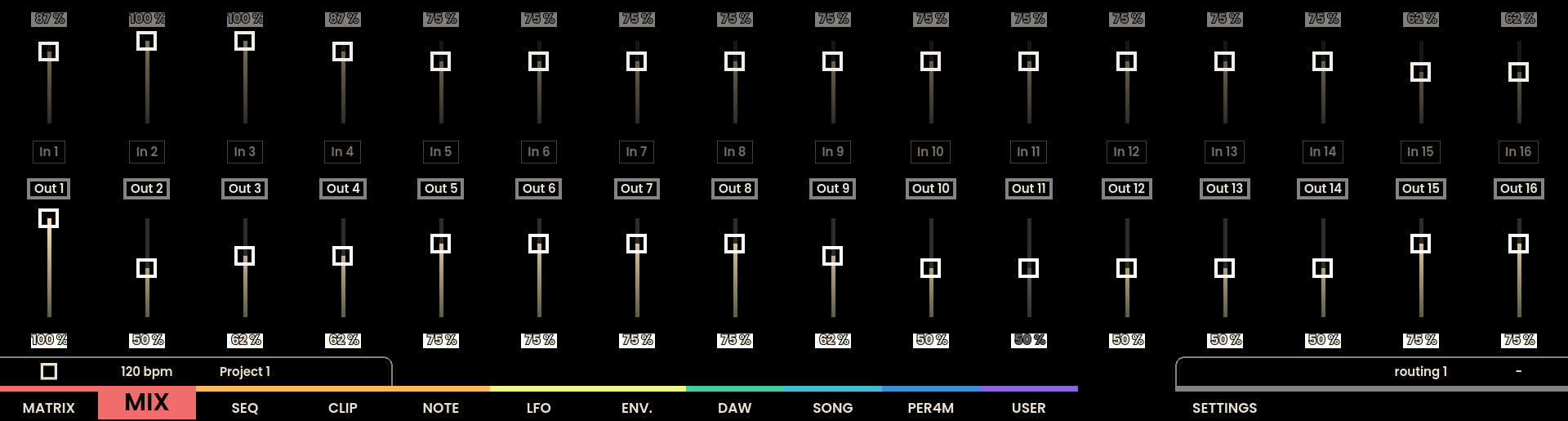
The Mix Page interface on Reliq’s display is divided into two vertical sections, similar to the Matrix Page. A total of 32 faders are displayed: 16 for the inputs (located at the top) and 16 for the outputs (located at the bottom). Each fader is color-coded to correspond to the group to which the input or output belongs.
The Grid Pads on the Mix Page offer similar visual feedback as the display. The top half of the grid represents the input levels, while the bottom half represents the output levels. Each column of the grid acts as a virtual fader, visually reflecting the current attenuation level for each input and output.
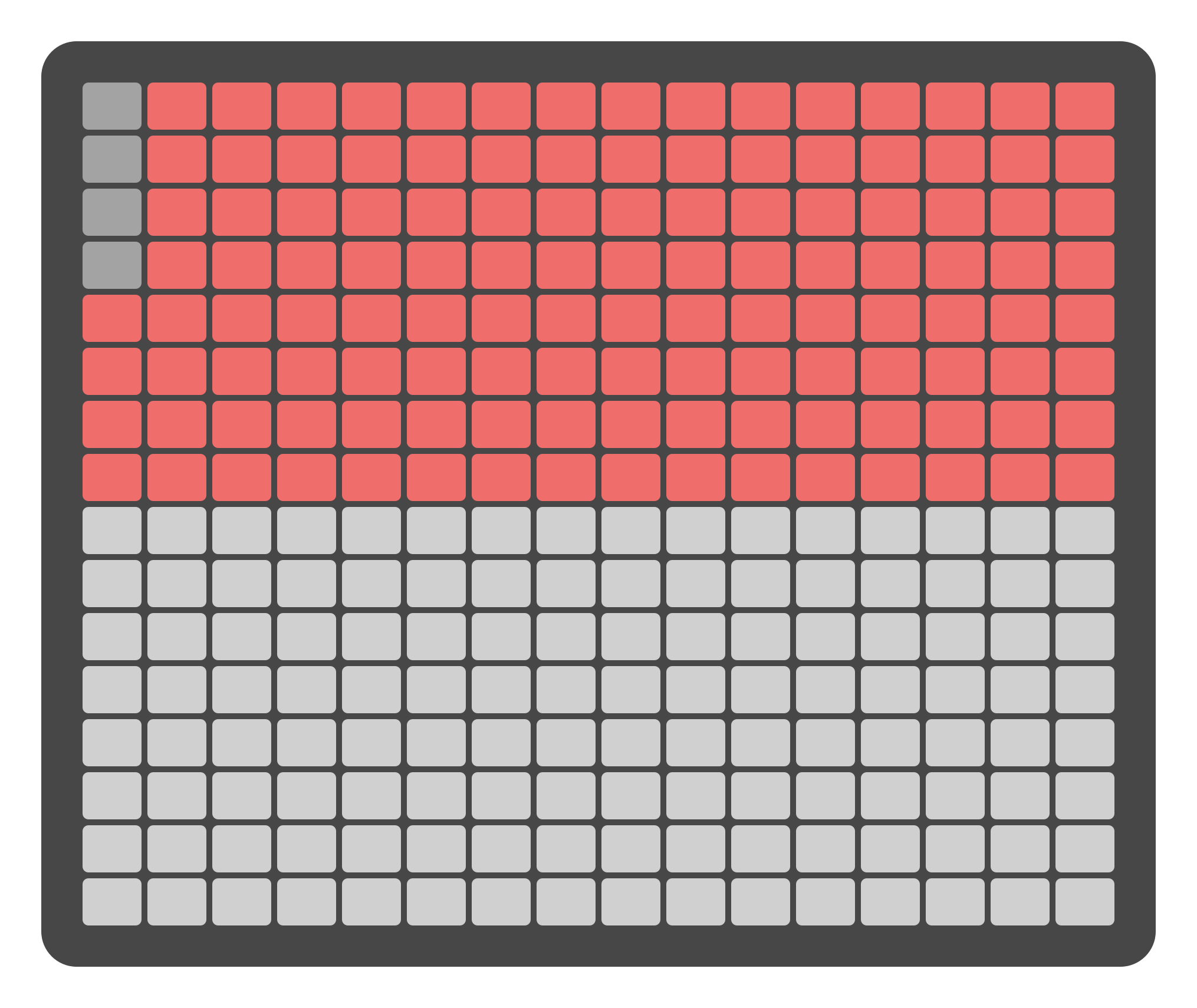
Attenuation adjustments can be made in two ways: using the Grid Pads for quick changes or using the Encoders above the display for more precise control. Clicking the Joystick Encoder upwards assigns the encoders to the inputs, while clicking it downwards assigns them to the outputs.
Attenuation Control
There are two primary methods for adjusting attenuation levels on the Mix Page:
Using the Grid Pads
The Grid Pads are divided into two sections: the top section represents virtual faders for the 16 inputs, and the bottom section represents virtual faders for the 16 outputs. Pressing a Grid Pad within each section adjusts the attenuation levels for the corresponding fader. This method allows for quick and efficient level adjustments.
Pressing SHIFT + the lowest pads in a section sets the levels to the lowest amount.
Note
Input and output levels on the Mix Page are expressed as percentages representing relative attenuation, not absolute signal volume. At 0%, signals are attenuated by approximately 63 dB on the inputs and 58 dB on the outputs. Some signal may still be faintly audible depending on the source and environment. This behavior is expected and reflects the analog nature of the mixer circuit design.
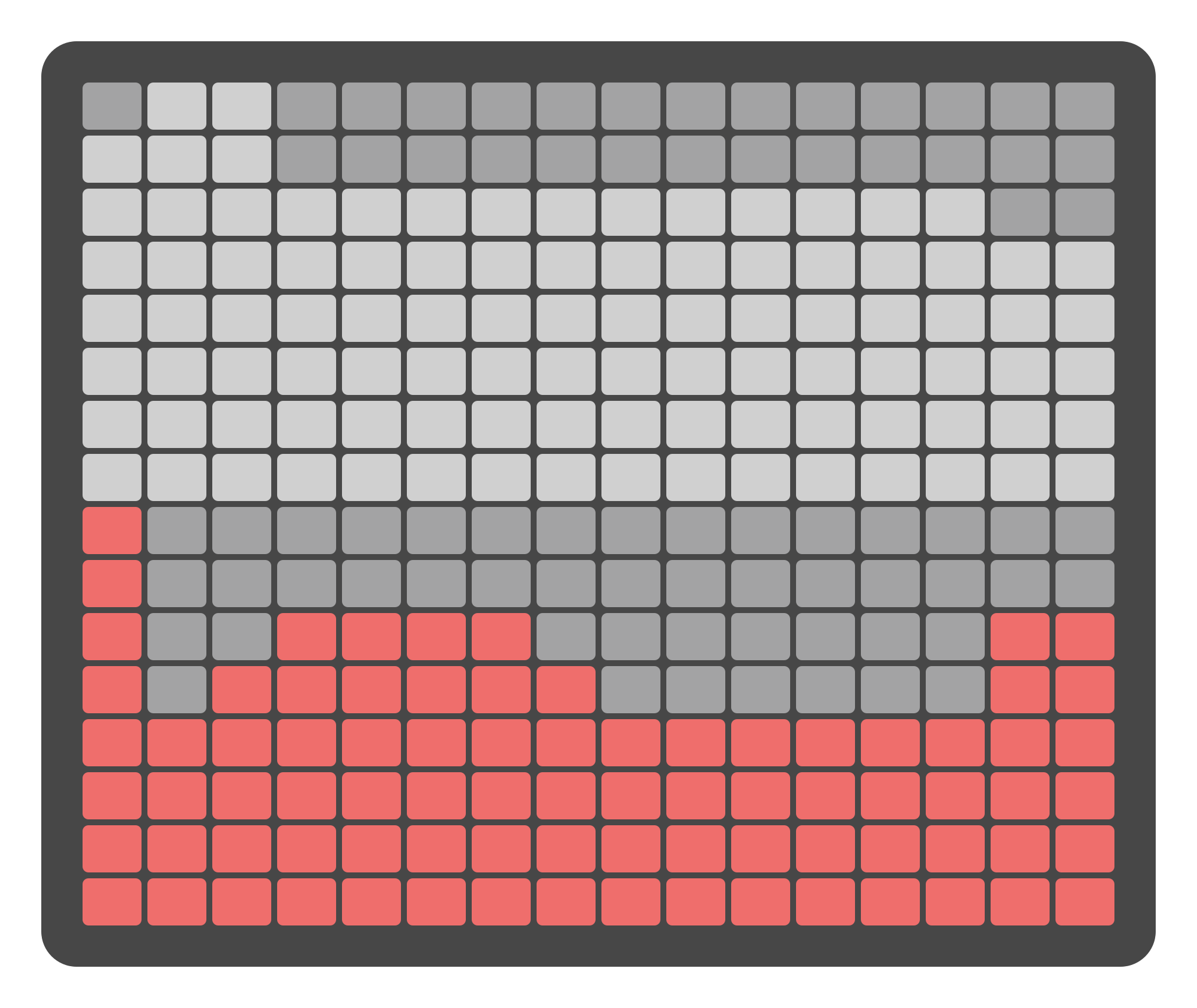
Grouped Channels
Grouped channels move proportionally when the level of any channel in the group changes. This preserves the ratio between grouped channels and allows mixing stereo or multichannel groups while keeping their original balance.
To change the balance between grouped channels without ungrouping them, long-press a channel’s pad to enter Parameter Lock, then press another pad in the same group/fader to set the relative adjustment.
Using the Encoders
The 16 physical encoders located above the screen can also control attenuation levels . Moving the Joystick Encoder upwards switches the main encoders to control the input levels, while moving it downwards switches them to control the output levels. This approach provides precise control over attenuation settings.
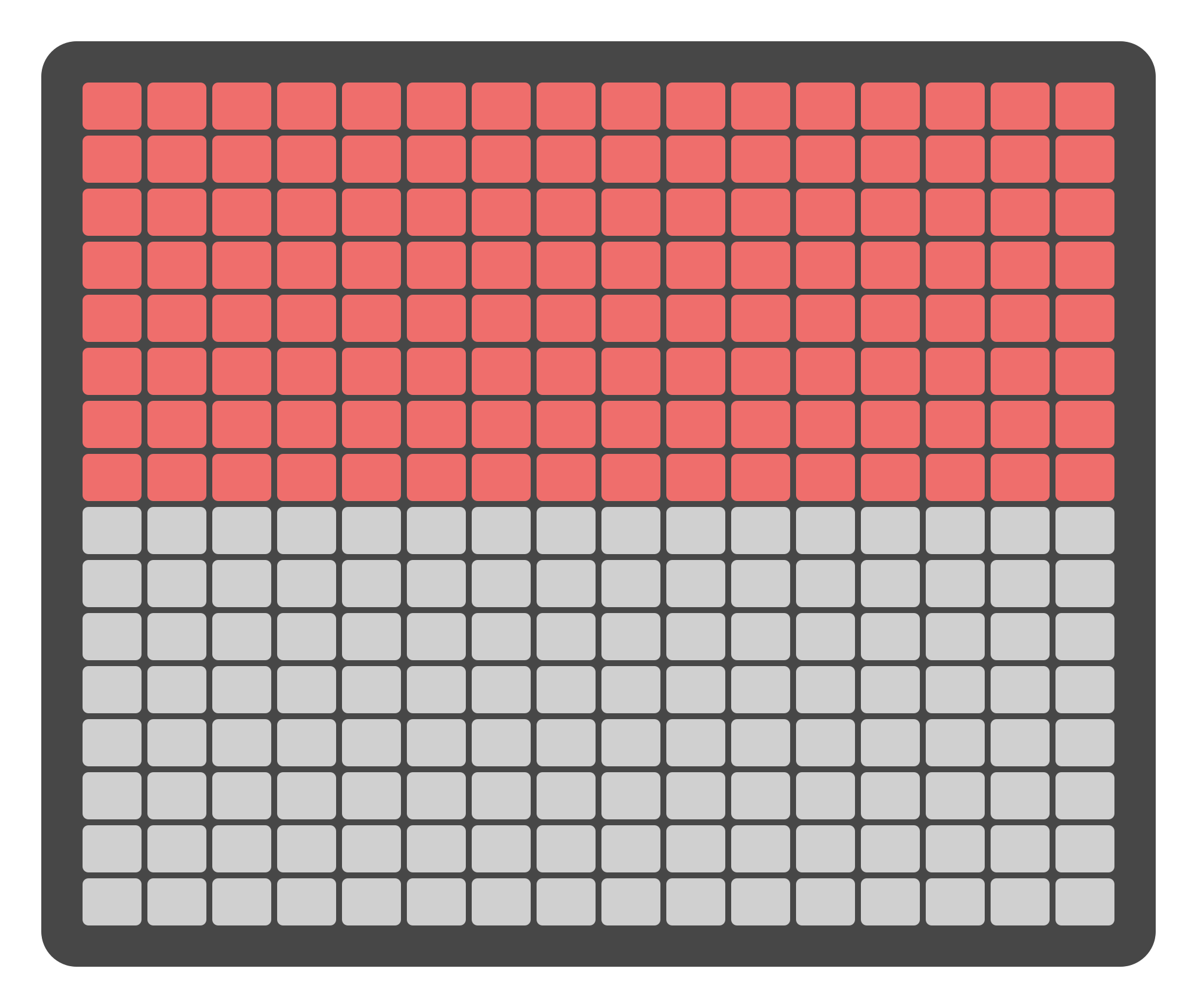
Select inputs levels with
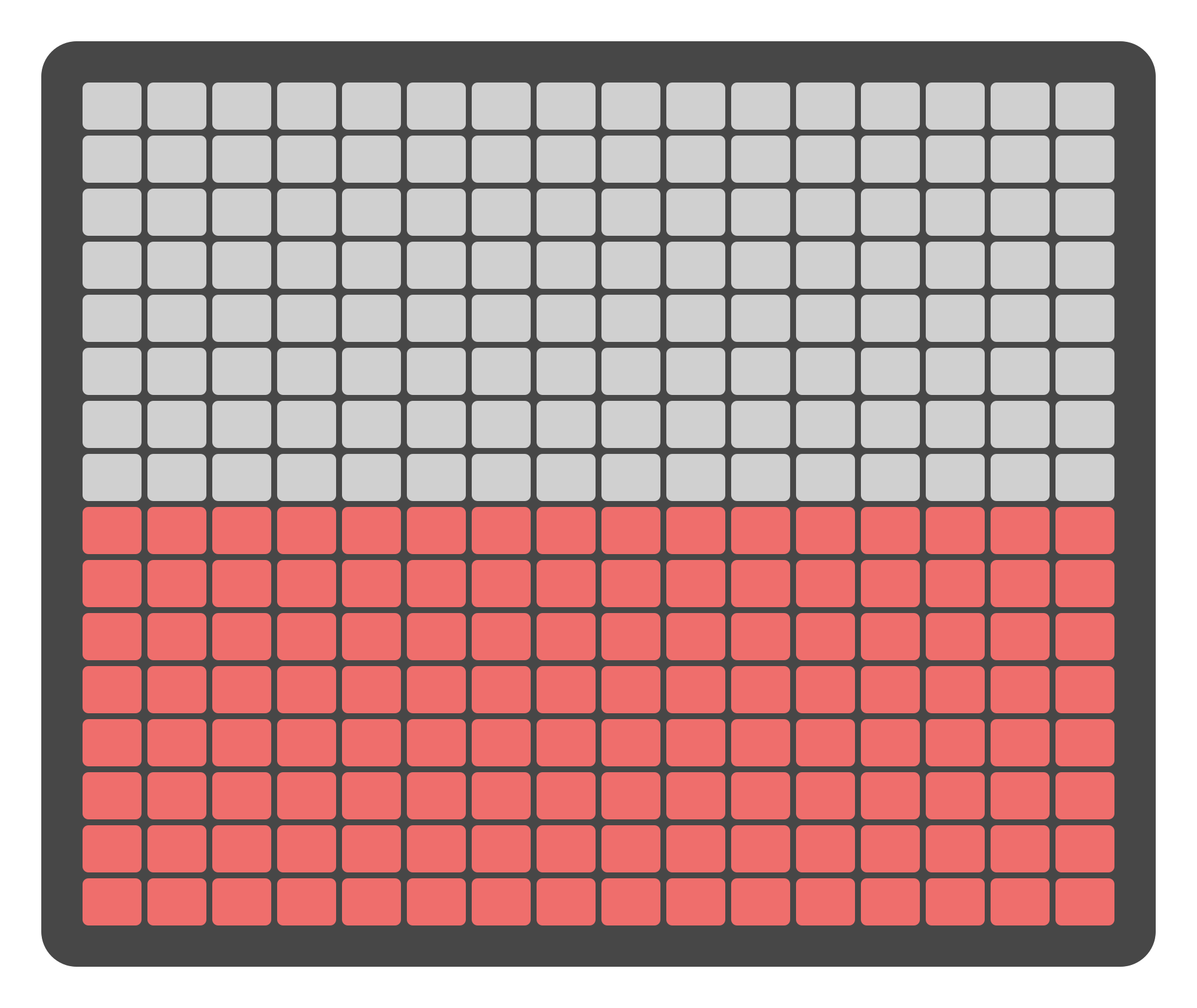
Select outputs levels with
Naming Inputs, Outputs and Routings from the Mix Page
The Mix Page allows for the naming of inputs, outputs, and routings similar to the Matrix Page. By pressing the Page Button below the routing or In/Out name, the reliq keyboard will open allowing for the naming of the selected item.
For more detailed information on naming Inputs, Outputs and Routings, refer to the Matrix Chapter.
Technical Specifications
Specification | Details |
|---|---|
Attenuation (Input) | 0 to ~63dB |
Attenuation (Output) | 0 to ~58dB |